1. Create Table
CREATE TABLE statement allows you to create new table in database.
The example code is given below.
create table profile(
id int,
name varchar(50),
birth_date date,
phone varchar(12),
gender varchar(1)
);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)2. Insert data in table
INSERT INTO statement is use to insert new record/data into table.
INSERT INTO profile (id, name, birth_date, phone, gender) VALUES (2, "Zaib", "1996-03-15", "9238975404", "M");Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
3. Insert multiple records at-once
INSERT INTO state is use to insert multiple new record/data into table.
INSERT INTO profile (id, name, birth_date, phone, gender) VALUES (1, "Usamn ali", "1990-08-26", "9238785094", "M", 18, "Karachi"), (2, "Aisha", "1997-06-12", "9238974468", "F", 19, "Lahore"), (3, "Awais", "1999-04-18", "9238975468", "F", 22, "Lahore"), (5, "Sahir", "2000-09-18", "9238973068", "M", 20, "Okara"), (6, "Sana jameel", "1992-04-22", "92389254046", "F", 18, "Karachi");Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)
4. Constants in mysql
Constant are also called constraints, mean we apply some restrictions on table's column.
following are constraints that we apply on columns.
1. NOT NULL 2. UNIQUE 3. DEFAULT 4. CHECK 5. FOREIGN KEY 6. PRIMARY KEY
1 NOT NULL: Column must have value.
2 UNIQUE : Column must have unique data (No duplication).
3 DEFAULT : If data not given to column while inserting than database automatically store default value in that column.
4 CHECK: we can apply checks for example user age must be greater and equal to 18.
Create table with constraints.
CREATE TABLE profile(
id INT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
birth_date DATE NOT NULL,
phone VARCHAR(12) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
gender VARCHAR(1) NOT NULL
);
5. Add column in existing table.
To add column in existing table, we us Alter TABLE <tablename> than ADD <columnname>.
ALTER TABLE profile
add age INT NOT NULL CHECK (age >= 18),
add city VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'Lahore';
6. Where clause with comparison operator.We use comparison operators with where clause where we need to fetch recordwith multiple check/conditions.SELECT * FROM profile
where (city = 'Lahore' or city = 'Okara') and gender = 'F';
7. IN and NOT IN operators
IN: Instead of multiple OR in query, we can make it simpler by using IN operator. we can add
multiple parameters in IN or NOT IN method
SELECT * FROM profile
where city in ('Lahore');
NOT IN: Instead of multiple (!=) in query, we can make it simpler by using NOT IN operator.
SELECT * FROM profile
where city not in ('Lahore');
8. BETWEEN and NOT BETWEEN operator.
BETWEEN operator checks value with in the range.
SELECT * FROM profile
where age between 18 and 21;
SELECT * FROM profile
where age not between 18 and 21;
Between:SELECT * FROM profile
where age between 18 and 21;
Between with date:SELECT * FROM profile
where birth_date between "1999-01-01" and "2001-01-01";
SELECT * FROM profile
where name between "a" and "t";
9. LIKE operator with wildcard patterns
LIKE operator is a logical operator that that specific pattern exist ingiven string or not.
Find name which start with 'a'.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name like 'a%';
Find name which start with 'a' or 'u'.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name like 'a%' or name like 'u%';
Find with case-sensitive get name with small starting character.
SELECT * FROM profile
where binary name like 'a%';
10. Regular expression patterns.Regular expression are use to find/check is specific pattern exist in speci--fic string of data or not. It is more advance than 'wildcard patterns'.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp 'ali';
Find column fields, whose value start with any specified patter. let say get me students name that start with 'ai'.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp '^ai';
Find a column field, whose value end with specifies pattern/string. let sayget me students name that ends with 'ali'.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp 'li$';
Get me the name which contain any of the given specified string.It willreturn all students name which containing specified string of 'ali' or 'jameel' or 'aisha'.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp 'ali|jameel|aisha';
We can also give multiple regular pattern to compare.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp 'jameel|^aisha|usa|ali$';
Get record which contains specified characterslet say we will find 'j' character containing names and than side-by-side'u' containing names.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp '[ju]';
It will return usman ali and sana jameel record.We can also make combination of regular expression that we want to find. let say 'ja' and 'sa' by passing '[js]a' in query.you can also make combination with this to: 'a[js]'. It make 'aj' and 'as'combinations.
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp '[js]a';
Find me student name whose value start with 'S' or either with 'A'
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp '^[as]';
Find me student name whose value end with 'S' or either with 'A'
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp '[as]$';
Find me students name with rang from a to j. what does it mean?.show me thename containing character with-the specifies range also contain anotherexpression within the range
SELECT * FROM profile
where name regexp '[b-r]sh';
11.Order BY and Group By in same queryFind total number of students in each city show count, city and order them descending order.
SELECT count(*) as total_students, city from profile group by city
order by city desc;
12. IS NULL and IS NOT NULL.Find me students list whose age is null(empty fields) or get non emptyfields
SELECT * from profile
where age is null;
SELECT * profile
where age is not null;;
13. LIMIT and OFFSET.It is not good practice to show/get all record at once in pages when yourdata increase to thousand of records. Than we use limit clause to specify how many number of record to fetch.What is the use of OFFSET: It is a value that define what is the startingpoint/where to start fetching of record from table.
we use this concept in pagination in websites.
SELECT * from profile
limit 0, 2;
'0' is offset mean it will start fetching from record one to two.'2' is the limit, number of record to fetch.
14. Commit and Rollback.Rollback: It use to rollback/previous state of record. mean, sometime we mistakenly update/change data in database, than later on we realize that we update/change wrong data. Mysql provides us a feature of rollback mean revert the changes.But: rollback revert all changes mean we only want to rollback one query but it rollback all previous executed queries.To overcome this problem mysql provide commit feature in database, by usingwe can limit step-back executed queries.NOTE: Rollback only work with: INSER, UPDATE and DELETE.
Commit: we can't revert changes based on queries we executed before commit.
SELECT * from profile;
commit;
update profile set age = 27 where id = 5;
rollback;
15. Primary and foreign Key constraints.Primary Key:ID refers as primary key of table. Primary key use to recognize each and individual data separately. Every primary key in table unique.While inserting new record you no need to insert value of id key.It automatically created.Foreign Key: Foreign key is use to create relationship between table.Foreign key must be primary key in other table.
Lets Create table with primary key constraint.
create table cities (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name varchar(50) NOT NULL,
primary key (id)
);
INSERT INTO cities (name)
values
('Lahore'),
('Karachi'),
('Islamabad'),
('Fasilabad');
Now add column cityID in profile table
alter table profile
add cityID INT NOT NULL;
Now add foreign key constraint on cityID column.NOTE: cityID must have matching record with city table otherwise constraintscreation gives error.
ALTER TABLE profile ADD CONSTRAINT fk_city
FOREIGN KEY (cityID) REFERENCES cities(id);
16. What is inner join?To get the the common(same) data of two tables than we use inner join to getthat common data.Inner join select/fetch record that have matching values.
SELECT p.name as student_name, c.name as city_name from profile p
inner join cities c
on p.cityID = c.id
we can also use where clause with join to further filter data.
SELECT p.name as student_name, c.name as city_name from profile p
inner join cities c
on p.cityID = c.id where c.name = 'Lahore';
Note we can use only 'join' in instead of inner join in query because bothhave same meaning.
17. what is left join?To get common data of two tables plus(+) all data from first(left) table 'A'than we use left join.
SELECT p.name as student_name, c.name as city_name from profile p
left join cities c
on p.cityID = c.id;
If table A record not match with Table B than no data fetch from table B
18. what is right join?To get matched common data from both left(A) and right(B) table plus(+)fetch all record from right(B) table.
SELECT p.name as student_name, c.name as city_name from profile p
right join cities c
on p.cityID = c.id;
19. what is right join?In cross join we do not have link/relation with foreign key constraint between two table.what does it mean we apply join(inner,left,right) on table based on primaryand foreign key but in cross join case we don't have these constraint.Than what cross join do? It create possible combination of record based on tables record. Let me giveyou an example.
See first three records are same but city name is different.
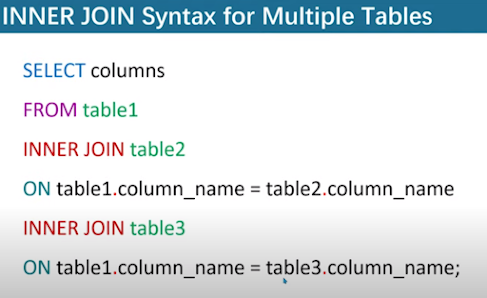
Query example20. what is multiple join?In multiple join we apply join on more than two tables.Let say table A,B and C.Let say table A have matched common record with table 'B' and Table 'A' also have matching record 'C'.Table A must have foreign keys of table B and C.
Multiple join syntax:21. How Group By work?Let say we have two tables, first is student table and second is city table.I want to know how many student belong to which city.,MAX,AVG,COUNT) to group rows together by common column values.
Group by syntax:Note: where clause must be before Group By.Order By clause must be after the Group By.
Having Clause:Let say i get the total number of student count according to city name.now i further want to apply condition on result(output).condition: show me cities record have more than ten students.
Mostly we use having clause with group by clause.Note: write having clause after groupby and before orderby clause.
22. What is SubQuery and Nested Query?When we add one query in another query. What does it mean ?When we want to get data from table A based on Table B.Example:Let say we have two tables Students and courses and we want to knowthose students who are enrolled in "Btech" course.
See we are fetching studenta those joined "Btech" course.Query Syntax:
See we use query in where clause to make condition.
Note: We can also use sub query with INSER,UPDATE,DELETE,SELECT commands.SubQuery with IN Operator:We use IN operator to fetch record based on child table multipleoptions e.g get me student those are enrolled either in "BTech" or "MBA".
Select with Exist Operator:How Exist command with child(sub) query work?When child command return record and fulfil condition, than parentcommand will return(show) record other wise not.
Same like that NOT EXIST work opposite to EXIST command.If child/sub query not return record tha parent table show recordother wise not.
23. What is UNION and UNION ALL ?When we want to combine two table result set/record we use these clauses.Combine the result set of two or more SELECT queries into single result set.But there are condition to use this clause in between tables.1) Number of selected column must be same in number, name and order.2) Constraints on column must be same to e.g data types int. varchar etc.Next question is what is the difference between UNION and UNION ALL ?UNION: It removes the dublicate data from the result set/record.UNION ALL: It not remove but instead of it fetch all result set/record from the tables.
Query Syntax:
Note: We can use where clause and sub queries and also we can use join butSELECTED column name, order and datatypes(constraints) mut be same.Where condition can be differentFor example: You can set cityname = "Lahore" in first table query andcityname = "Delhi" in second table query.
Query with inner join:
24. What is IF clause?IF clause is an conditional expression in sql queries. Mean we can putcondition to verify before updating and selecting/fetching record.
Note: we use IF clause with SELECT and UPDATE queries.
Example1:Let say i want to give bonus to my sales employees of 1000 cash butcondition is employee sale must be equal or grater than 10 thousandand 500 to others.Query:
Update employee SET bonus = IF(sale_amount > 5000,1000,500);
Example2:Let say we have students result record in table, based on mark we want tocheck which student is pass or fail.
See new column will add in showing result table.Let see how we write it in queries to fetch this type of record.
Query Syntax:
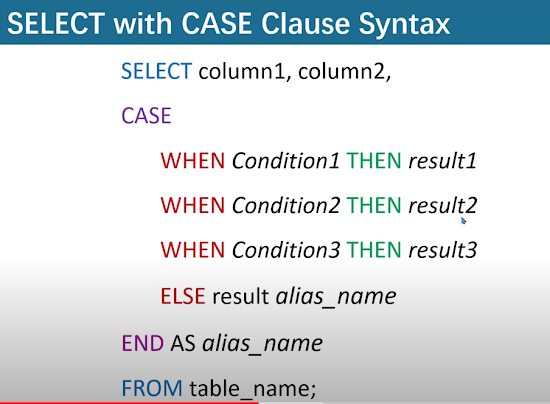
25. What is CASE clause?CASE clause is use to provide conditional logic within the query.It allows you to perform different action on specific condition. Basedon condition you can create custom result from your table record.
Note: CASE clause is only use with SELECT, UPDATE statement.
Example:
Query Syntax:
Note that the CASE clause can be used in other parts of the SQL query, such as in the WHERE clause or ORDER BY clause, to provide more complex conditional logic in your queries.
Example query:
Update record with CASE clause.We can update multiple record in table using CASE clause in single query.
Example Query:
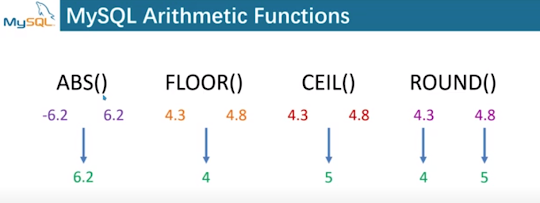
26. Arithmetic Function in Mysqli
Alter CommandAlter command we use when we want to make modification in our table.With the help of alter command what we can do is discuss below. Features of alter command:What we can do with alter command?
Alter Command syntax:
In datatype we can define any of check, default values, int/varcharor null etc.
Alter table queries:1) Add column in table
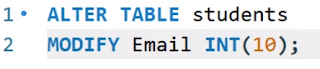
2) Modify datatype of column
3) Reorder column position in table
4) Add constant in columnwe adding unique constant in existing column
Same way we can also add primary key constraint as well.5) Rename column name
6) Drop/Delete column
7) Rename table name
8) Set auto-increment start valueMost of the time when we delete some record from table and afterthat when we add new record, its id value start/set deleted recordid next value.to overcome this problem we need to run this query.To keep the order increment same.
27. View CommandWe create view command to shorten our long, complex queries.Mysql store our queries in the form of view in view table.we simply select that view to fetch our record from database.
1. Lets create viewway1:CREATE VIEW <viewname>AS<our normal query>
than we run that query like so,SELECT * FROM <viewname>2. Alter view queryALTER VIEW <viewname>AS<new query>
way2:We can create and update our view like so3. CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW <viewname>AS<you query>
4. Rename view nameRENAME TABLE <oldname>TO <newname>5. Drop viewDROP VIEW <viewname>Advanteges: codesimplicity, add extra layer of security.disadvantage: performance down: Because first databasecontroller find the view than run the desire view query 28. IndexingWhen we want to search data from database as fast as compare to normalfetching/selecting of data that take much time than we use indexing.How indexing work?We create index table in our database server and add columns of table mostof the time we use to search record in that index table.How to Create index?Syntax:CREATE INDEX <index_name>ON <table_name>(coumn1,column2,column3...);
this index will permanently save in our database.
How to delete any index?DROP INDEX <index_name> ON <table_name>
Guidelines to make-sure for creating index table.1. No need to add primary and unique constant in index table because theyalready index data.2. indexed those column on which you want to apply searching.3. indexed apply on those tables that are linked with joins.4. Avoid NULL column for indexing.5. Small table do not require indexing.
Show index column from tableSHOW INDEX FROM <table_name>
Practice command before interview
Create table of employee
Sql Command:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS employees (
id INT(255) NOT NUll AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY Key,
department varchar(255) NOT NULL,
name varchar(255) NOT NULL,
salary INTEGER(255) NOT NULL,
status ENUM('active','deactive'),
joining_date DATE
);
Insert record in employees table
INSERT INTO employees (`department`,`name`,`salary`,`status`,`joining_date`)
VALUES
('brain_soft','Adnan',120000,'active','2023-11-14'),
('brain_soft','Ghazanfer',100000,'active','2023-11-13'),
('brain_soft','Humza',95000,'active','2023-11-12'),
('NOC','Farooq',110000,'active','2023-11-09'),
('NOC','Sohail',200000,'active','2023-10-14'),
('BTEL','Amir',80000,'deactive','2023-09-09'),
('BTEL','Ehsan',180000,'active','2023-03-10')
;
Get me avarage salary of department paying to their employees
Sql Command:
SELECT department, AVG(salary) as average_salary FROM `employees`GROUP By department;
Get me second high salary of the employee
SELECT
name,
salary
FROM
employees
WHERE
salary = (
SELECT
MAX(salary)
FROM
employees
WHERE
salary < (
SELECT
MAX(salary)
FROM
employees
)
)




































Comments
Post a Comment