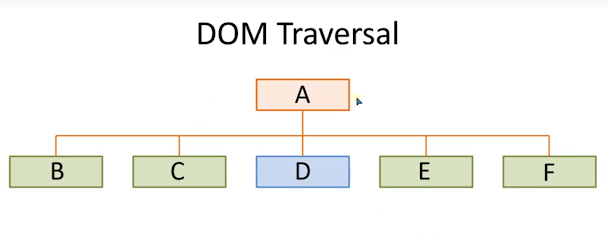
Tree Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>DOM Navigation</title>
</head>
<style>
#outer{
width: 800px;
height: auto;
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 150px auto;
padding: 10px;
border-radius: 1rem;
}
#inner{
width: 600px;
height: 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
border-radius: 1rem;
margin: 0px auto;
margin-bottom: 100px;
padding: 10px;
}
#inner {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
flex-direction: row;
align-items: center;
}
.child{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border: 1px solid black;
border-radius: 1rem;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
<body>
<center>
<h1>DOM Trversal Methods</h1>
</center>
<div id="outer">
<h1>Outer</h1>
<div id="inner">
<h2>Inner</h2>
<div class="child" id="a">A</div>
<div class="child" id="b">B</div>
<!-- <p>This is comment</p> -->
<div class="child" id="c">C</div>
<div class="child" id="d">D</div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
// 1 ParentElement
/*
It will print parent element with its all children
*/
var element;
element = document.querySelector("#inner").parentElement;
console.log(element);
// change color
element = document.querySelector("#inner").parentElement.style.background = 'pink';
console.log(element);
// if parent element exist it will return other wise it return null
// 2 parentNode
// parentNode method always return somthing if parant element not exist.
element = document.querySelector("#outer").parentElement;
console.log(element);
// 3 Children
// is mein hum parent ki help se children ko target krte han.
element = document.querySelector("#outer").children;
console.log(element);
element = document.querySelector("#inner").children;
console.log(element);
// chnange font size and color of children
element = document.querySelector("#inner").children[0].style.color = 'red';
element = document.querySelector("#inner").children[0].style.fontSize = '40px';
element = document.querySelector("#inner").children[3].style.color = 'white';
element = document.querySelector("#inner").children[3].style.background = 'red';
element = document.querySelector("#inner").children[3].innerText = 'Child-C';
console.log(element);
// it will return array of length with elements
// Note Children method only return us html tags but childNode return us tag with text (Text men every other element it take as text see example)
element = document.querySelector("#inner").childNodes;
console.log(element);
element = document.querySelector("#inner").childNodes[11].style.background="white";
console.log(element);
// 4 firstElementChild
// il will return first childer of parent elemet
element = document.querySelector("#inner").firstElementChild.innerHTML;
console.log(element);
element = document.querySelector("#outer").firstElementChild;
console.log(element);
// chnange color
element = document.querySelector("#outer").firstElementChild.style.background="silver";
element = document.querySelector("#outer").lastElementChild.style.background="silver";
// get last chld of inner
element = document.querySelector("#inner").lastElementChild;
console.log(element);
// 5 firstChild And lastChild
// difference b/t firstElementChild and firstChild
// firstElementChild only targer firt available tag and firstChild will target first element either it is text please check example of childNodes .
element = document.querySelector("#inner").firstChild;
console.log(element);
element = document.querySelector("#inner").lastChild;
console.log(element);
// 6 nextElementSibling
element = document.querySelector("#c").nextElementSibling;
console.log('nextElementSibling');
console.log(element);
// 7 previousElementSibling
element = document.querySelector("#c").previousElementSibling;
console.log('previousElementSibling');
console.log(element);
// 8 nextSibling and previousSibling
// Note: These properties target tags and well as text
</script>
</body>
</html>
Comments
Post a Comment